Call Center Software CRM: A Comprehensive Guide
Call center software CRM revolutionizes customer interaction and operational efficiency. This powerful technology integrates customer relationship management with call center functionalities, streamlining processes and enhancing agent performance. From managing customer interactions to analyzing performance metrics, call center software CRM offers a holistic solution for optimizing customer service and boosting business growth. This guide explores its core features, integration capabilities, and impact on both customer experience and overall ROI.
Understanding the nuances of call center software CRM is crucial for businesses aiming to elevate their customer service strategies. This involves selecting the right software, integrating it seamlessly with existing systems, and leveraging its data-driven insights to enhance agent productivity and customer satisfaction. We’ll delve into the key features, best practices, and future trends shaping this dynamic field.
Defining Call Center Software CRM
Call center software CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems are specialized software solutions designed to manage and improve all aspects of a call center’s operations. They integrate various functionalities to streamline communication, enhance customer service, and boost overall efficiency. These systems go beyond basic contact management, offering a comprehensive suite of tools tailored to the unique demands of a high-volume call environment.
Core functionalities of a call center software CRM system typically include features for managing customer interactions, tracking calls, analyzing performance metrics, and improving agent productivity. These systems often integrate with other business tools to provide a holistic view of the customer journey and operational performance.
Core Functionalities of Call Center Software CRMs
Call center software CRMs offer a range of functionalities designed to optimize call center operations and enhance customer experience. These functionalities work together to provide a comprehensive solution for managing customer interactions and improving business outcomes.
Key features commonly found include:
- Call Routing and Queuing: Intelligent call routing distributes incoming calls to the most appropriate agents based on various factors, such as agent skills, availability, and call type. Queuing systems manage calls efficiently, minimizing wait times for customers.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): IVR systems automate initial interactions, guiding callers through self-service options and directing them to the right agents, reducing agent workload and improving customer satisfaction.
- Call Recording and Monitoring: Recording calls allows for quality assurance, training purposes, and dispute resolution. Monitoring tools provide real-time oversight of agent performance, enabling supervisors to identify areas for improvement.
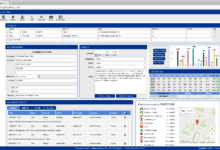
- Customer Data Management: A centralized database stores comprehensive customer information, providing agents with a complete view of each customer’s history and interactions, facilitating personalized service.
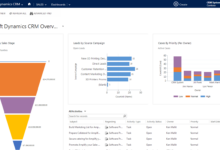
- Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reports and dashboards provide insights into key performance indicators (KPIs), such as average handling time, call resolution rates, and customer satisfaction scores, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Agent Performance Management: Tools for tracking agent performance, providing feedback, and identifying training needs, contribute to improved agent skills and productivity.
- Integration with other systems: Seamless integration with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, helpdesk software, and other CRMs, provides a unified view of customer interactions across all channels.
Differences Between Standalone CRM and Call Center Software CRM
While both standalone CRMs and call center software CRMs manage customer data, their functionalities and focus differ significantly. Standalone CRMs primarily focus on managing customer interactions and data across various channels, but they lack the specialized features required for high-volume call center environments. Call center software CRMs, on the other hand, are specifically designed to handle the unique demands of call centers, offering advanced features for call management, routing, and agent performance monitoring. They are optimized for handling large call volumes and ensuring efficient call handling processes.
Examples of Features in Call Center Software CRMs
Different call center software CRMs offer varying features to cater to diverse business needs and sizes. For example, some systems may offer advanced predictive dialing capabilities to automate outbound calls, while others may focus on sophisticated reporting and analytics tools for performance monitoring. Some systems may offer advanced features like sentiment analysis of customer calls to better understand customer satisfaction levels. Integration capabilities vary widely, with some systems offering integration with a broad range of third-party applications, while others have more limited integration options.
Comparison of Popular Call Center Software CRMs
The following table compares three popular call center software CRMs based on their key features, pricing models, and integration capabilities. Note that pricing can vary depending on the number of users and specific features selected.
| Software Name | Key Features | Pricing Model | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Five9 | Cloud-based call center software, IVR, call recording, workforce management, analytics dashboards | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Integrates with various CRM, ERP, and other business applications via APIs |
| Talkdesk | Cloud-based contact center platform, omnichannel routing, AI-powered features, workforce optimization tools | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Integrates with Salesforce, Zendesk, and other popular applications |
| Genesys Cloud | Cloud-based contact center solution, omnichannel capabilities, AI-driven features, workforce engagement management | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Extensive integration capabilities with various CRM, ERP, and other applications |
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration with your existing business tools is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of your call center software CRM. A well-integrated system streamlines workflows, reduces data entry, and provides a unified view of your customer interactions, ultimately leading to improved customer service and increased operational efficiency. Failure to integrate effectively can result in data silos, duplicated effort, and a fragmented customer experience.
Effective integration ensures that data flows smoothly between your call center software CRM and other critical business systems, eliminating manual data transfer and reducing the risk of errors. This allows for a more holistic understanding of customer behavior and preferences, leading to more informed decision-making and improved business outcomes. However, integrating a new system, especially with older, legacy systems, presents unique challenges.
Challenges of Integrating with Legacy Systems
Integrating a modern call center software CRM with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming. Legacy systems often lack the APIs or standardized data formats necessary for seamless integration. Data migration can be challenging, requiring careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or corruption. Furthermore, older systems may have limited scalability and flexibility, potentially hindering the ability of the integrated system to handle future growth. Compatibility issues between different software versions and technologies can also arise, requiring significant technical expertise to resolve. For example, a company using a decades-old accounting system might find it difficult to integrate with a modern CRM due to incompatible data structures and limited API capabilities. This may require custom integration solutions or even a phased approach involving system upgrades or replacements.
Best Practices for Email Marketing Platform Integration
Successful integration with email marketing platforms enhances customer communication and improves marketing campaign effectiveness. Real-time data synchronization between the call center software CRM and the email marketing platform allows for personalized email campaigns based on recent customer interactions. For instance, a customer who called to inquire about a specific product can receive a targeted email promoting that product shortly after the call. Best practices include using APIs to automate data exchange, ensuring data consistency through regular synchronization, and implementing robust error handling to prevent data loss or corruption. Careful mapping of customer data fields between the two systems is crucial to maintain data integrity and accuracy. A company leveraging this integration might see a significant increase in email open rates and conversion rates due to the highly targeted nature of the campaigns.
Data Flow Between Call Center Software CRM and Accounting Software
The following flowchart illustrates the data flow between a call center software CRM and accounting software.
[Descriptive Flowchart]
Imagine a flowchart with two main boxes: “Call Center Software CRM” and “Accounting Software.” Arrows connect them. From the CRM box, an arrow labeled “Invoice Data (Customer ID, Amount, Date)” points to the Accounting Software box. Another arrow, labeled “Payment Data (Transaction ID, Amount, Date, Customer ID)” goes from the Accounting Software box back to the CRM box. A third arrow, labeled “Customer Data (Customer ID, Contact Information)” flows from the CRM to the Accounting Software. This illustrates how customer data, invoice details, and payment information are exchanged between the two systems, automating crucial financial processes. This automated data flow eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and provides a more efficient and accurate financial record-keeping system. For example, when a customer makes a payment through the CRM, the data is automatically updated in the accounting software, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reconciliation.
Agent Productivity and Performance
Effective call center software CRM significantly impacts agent productivity and overall performance. By streamlining workflows and providing valuable insights, these systems empower agents to handle more calls efficiently and improve customer satisfaction. This section details key metrics, feature benefits, and reporting capabilities that contribute to enhanced agent performance.
Key Metrics for Measuring Agent Performance
Measuring agent performance requires a multifaceted approach. Key metrics provide a comprehensive view of individual and team effectiveness. These metrics should be regularly tracked and analyzed to identify areas for improvement and recognize top performers.
- Average Handle Time (AHT): This measures the average duration of a call, encompassing talk time, hold time, and after-call work. Lower AHT generally indicates higher efficiency.
- Calls Handled per Hour: This metric reflects the number of calls an agent successfully completes within an hour. Higher numbers suggest greater efficiency and call-handling capacity.
- First Call Resolution (FCR): This crucial metric tracks the percentage of calls resolved on the first attempt. High FCR rates indicate efficient problem-solving and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measured through surveys or feedback mechanisms, CSAT reflects customer perception of the agent’s service. High CSAT scores demonstrate effective communication and problem-solving skills.
- Adherence to Schedule: This metric assesses how closely agents adhere to their assigned schedules, reflecting punctuality and time management.
How Call Center Software CRM Features Improve Agent Efficiency
Call center software CRMs are designed to enhance agent efficiency through several key features. These features automate tasks, provide readily accessible information, and streamline workflows, resulting in improved productivity and reduced call handling times.
- Automated Call Routing: Intelligent routing systems direct calls to the most appropriate agent based on skills, availability, and call type, minimizing wait times and improving first-call resolution.
- Integrated Knowledge Base: Easy access to a comprehensive knowledge base allows agents to quickly find answers to customer queries, reducing research time and improving resolution rates. This could include FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and product information.
- Screen Pops: Automatic display of customer information (history, past interactions, account details) upon call initiation, allowing agents to personalize interactions and address customer needs efficiently.
- Call Recording and Monitoring: Call recording enables quality assurance and coaching opportunities, while real-time monitoring allows supervisors to offer assistance and guidance as needed.
- Ticketing and Case Management Systems: Streamlines handling of complex issues that require follow-up, ensuring efficient tracking and resolution of customer problems.
Reporting and Analytics Dashboards in Call Center Software CRMs
Different call center software CRMs offer varying reporting and analytics dashboards, providing insights into agent performance and operational efficiency. The choice depends on the specific needs and size of the call center.
- Basic Dashboards: These typically display key metrics like AHT, calls handled, and FCR, offering a high-level overview of agent performance.
- Advanced Dashboards: These dashboards offer more granular data, including individual agent performance across various metrics, trend analysis, and customizable reports. They may also incorporate real-time data visualizations.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allow users to select and arrange specific metrics and visualizations based on their needs, offering flexibility and tailored insights.
Features Enhancing Agent Training and Knowledge Base Access
Effective agent training and readily available knowledge resources are crucial for optimal performance. Call center software CRMs incorporate features to support these aspects.
- Integrated Training Modules: Some CRMs offer built-in training modules that provide agents with on-demand access to learning materials, improving knowledge retention and reducing the need for traditional classroom training.
- Searchable Knowledge Base: A well-organized and easily searchable knowledge base empowers agents to quickly find relevant information, ensuring accurate and efficient responses to customer inquiries.
- Performance Feedback Mechanisms: CRMs can facilitate regular performance feedback through automated reports, supervisor comments, and peer reviews, contributing to continuous improvement.
Customer Experience Enhancement
Call center software CRM significantly improves customer satisfaction by streamlining interactions, personalizing service, and enabling proactive support. By centralizing customer data and automating processes, it empowers agents to provide efficient and effective assistance, leading to happier customers and increased loyalty.
Call center software CRM directly impacts customer satisfaction by reducing wait times, improving first-call resolution rates, and providing a more consistent and personalized experience across all touchpoints. This results in higher customer satisfaction scores and a stronger brand reputation.
Personalized Customer Interactions
Features such as automated greetings using customer name, personalized email templates based on past interactions, and offering tailored product recommendations based on purchase history directly contribute to a more personalized experience. For example, a customer who frequently purchases running shoes might receive a proactive email about a new line of running socks, while a customer who primarily buys office supplies might receive targeted offers on new stationery products. This targeted approach makes customers feel valued and understood, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
Proactive Customer Needs Addressing
Call center software CRM facilitates proactive customer service through features like predictive analytics and automated alerts. By analyzing customer data, the software can identify patterns and predict potential issues. For example, if a customer has consistently experienced delays in receiving shipments, the system might proactively alert the agent to offer expedited shipping on their next order. Similarly, the system might flag customers who are nearing the end of their contract term, allowing agents to reach out and offer renewal options before they churn. This proactive approach demonstrates care and prevents potential problems before they arise.
Complex Customer Issue Resolution Scenario
Imagine a customer experiencing difficulties with a complex technical issue involving their newly purchased software. Using the call center software CRM, the agent can access the customer’s complete history, including previous interactions, purchase details, and technical support requests. This allows the agent to quickly understand the context of the problem and provide tailored assistance. The CRM might even suggest relevant knowledge base articles or troubleshooting steps based on similar past issues. The agent, armed with this information, can efficiently guide the customer through the solution, resolving the issue quickly and effectively. If the problem proves too complex, the CRM facilitates seamless escalation to a higher-tier support team, ensuring the customer receives the appropriate level of assistance while maintaining a consistent and informed experience throughout the process. This efficient and comprehensive approach minimizes frustration and enhances customer satisfaction.
Security and Data Privacy
In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding sensitive customer data is paramount for any call center utilizing CRM software. Reputable call center CRM solutions prioritize robust security measures to protect both the business and its customers. A comprehensive security strategy is essential to maintaining customer trust and complying with stringent data privacy regulations.
Data encryption and access control are fundamental components of a secure call center CRM system. These measures, along with regular security audits and employee training, minimize the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format, rendering it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals even if a breach occurs. This typically involves encrypting data both in transit (while being transmitted over networks) and at rest (while stored on servers or databases). Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), limit access to sensitive data based on an individual’s role and responsibilities within the organization. For instance, a customer service agent might have access to customer contact information and interaction history, but not to financial data, which would be restricted to authorized personnel in the finance department. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) further enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized logins.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Adherence to data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in California is crucial. These regulations mandate specific security measures and data handling practices. For example, GDPR requires organizations to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data, including data encryption and access control, as well as providing individuals with the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal data. CCPA similarly requires businesses to provide consumers with transparency regarding the collection and use of their data and to allow them to opt out of the sale of their personal data. Compliance often necessitates detailed documentation of data processing activities, regular security assessments, and incident response plans.
Security Policy for Handling Sensitive Customer Data
A comprehensive security policy is essential for managing sensitive customer data within a call center CRM environment. This policy should outline procedures for data access, storage, and disposal, along with incident response protocols. Specific elements of such a policy might include:
* Data Access Restrictions: Clearly define which employees have access to specific types of data, based on their roles and responsibilities. Implement robust access control mechanisms to enforce these restrictions.
* Data Encryption: Mandate the encryption of all sensitive customer data, both in transit and at rest. Specify the encryption algorithms and key management practices to be used.
* Data Storage: Define secure storage locations and procedures for storing customer data. This includes specifying backup and recovery procedures to ensure data availability in case of system failures or disasters.
* Data Disposal: Outline procedures for securely disposing of customer data when it is no longer needed. This might involve secure deletion or data sanitization techniques.
* Incident Response: Establish a clear incident response plan to handle security breaches or data leaks. This plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, and remediating security incidents, as well as for notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities.
* Employee Training: Regularly train employees on security best practices and the importance of protecting customer data. This training should cover topics such as password security, phishing awareness, and data handling procedures.
Cost and ROI Considerations
Investing in call center software CRM involves a significant financial commitment. Understanding the various pricing models, associated costs, and potential return on investment is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will outline the key cost factors and provide a framework for evaluating the financial viability of implementing a call center CRM system.
Pricing Models for Call Center Software CRMs
Call center software CRMs typically utilize one of two primary pricing models: subscription-based and one-time purchase. Subscription models, often tiered based on features and the number of agents, offer predictable monthly or annual costs. One-time purchase models involve a larger upfront investment but eliminate recurring fees. The optimal choice depends on the organization’s budget, anticipated growth, and long-term needs. A small business with limited resources might favor a lower-tiered subscription model, while a larger enterprise with substantial capital might find a one-time purchase more cost-effective in the long run, provided they can manage the system’s ongoing maintenance and upgrades.
Factors Influencing the Total Cost of Ownership
The total cost of ownership (TCO) extends beyond the initial software purchase or subscription fee. Several factors contribute to the overall expense. These include implementation costs (consulting, training, data migration), ongoing maintenance and support fees, hardware and infrastructure requirements (servers, computers, network bandwidth), and potential integration costs with existing systems. For example, integrating a new CRM with a legacy billing system might require custom development, adding significantly to the TCO. Regular software updates and security patches are also ongoing expenses. It is crucial to account for all these elements when budgeting for a call center CRM.
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the ROI of a call center CRM involves comparing the total costs against the anticipated benefits. Benefits might include increased agent productivity, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs (e.g., fewer dropped calls, shorter call handling times), and enhanced sales conversion rates. A simple ROI calculation can be expressed as:
ROI = (Net Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs * 100%
For example, if a company invests $10,000 in a CRM and experiences a $20,000 increase in annual revenue due to improved efficiency and customer retention, the ROI would be:
ROI = ($20,000 – $10,000) / $10,000 * 100% = 100%
This demonstrates a significant return on the investment. However, this is a simplified calculation. A more comprehensive analysis would include detailed projections of all costs and benefits over a longer time horizon.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider both tangible and intangible benefits. A template could include the following:
| Cost Factor | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Software License/Subscription | $ |
| Implementation Costs | $ |
| Training Costs | $ |
| Hardware/Infrastructure | $ |
| Integration Costs | $ |
| Maintenance & Support | $ |
| Total Costs | $ |
| Benefit Factor | Estimated Benefit (Annual) |
|---|---|
| Increased Agent Productivity | $ |
| Improved Customer Satisfaction | $ (estimated based on improved retention rates) |
| Reduced Operational Costs | $ |
| Enhanced Sales Conversion | $ |
| Total Benefits (Annual) | $ |
This template allows for a clear comparison of costs and benefits over a specified period, facilitating a data-driven decision about CRM implementation. Remember to use realistic estimates based on your specific business context and projected growth.
Future Trends in Call Center Software CRM
The call center software CRM landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-increasing demands for efficient and personalized customer service. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and stay ahead of the competition. This section will explore key future directions shaping the future of call center software CRMs.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Call Center Software CRM
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming call center operations. AI-powered chatbots are handling increasingly complex customer inquiries, providing instant support and freeing up human agents to focus on more intricate issues. ML algorithms analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and predict future behavior, enabling proactive customer service and personalized outreach. For example, predictive analytics can identify customers likely to churn and trigger targeted interventions to retain them. Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows for more natural and intuitive interactions between customers and the system, leading to improved customer satisfaction. These technologies are not simply automating tasks; they’re enhancing the entire customer journey.
The Impact of Automation on Call Center Operations
Automation is streamlining various call center processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks such as data entry and scheduling, freeing up agents to focus on higher-value interactions. Intelligent automation combines AI and RPA to create sophisticated workflows that adapt to changing circumstances. For instance, an automated system could route calls based on customer history and the agent’s expertise, ensuring efficient call handling and reducing wait times. This increased efficiency translates to improved agent productivity and reduced operational costs. Companies like Amazon have been at the forefront of implementing such automation strategies in their customer service departments.
The Role of Cloud-Based Call Center Software CRMs
Cloud-based call center software CRMs offer several advantages over on-premise solutions. Scalability is a key benefit; businesses can easily adjust their capacity based on demand, adding or removing resources as needed. This flexibility is particularly important for businesses experiencing seasonal fluctuations in call volume. Cloud-based systems also offer enhanced accessibility, allowing agents to work remotely and access customer data from anywhere with an internet connection. Furthermore, cloud providers often handle security and maintenance, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. Salesforce Service Cloud and Zendesk are prime examples of widely adopted cloud-based CRM solutions.
Predictions for the Future of Call Center Software CRM and its Impact on Customer Service
The future of call center software CRM points towards a more integrated, intelligent, and personalized customer experience. We can expect to see increased use of AI-powered tools for proactive customer service, predictive analytics for anticipating customer needs, and omnichannel integration for seamless interactions across various channels. The role of human agents will evolve, shifting from primarily handling transactional tasks to focusing on complex problem-solving and building customer relationships. This will lead to more personalized and empathetic customer service, fostering stronger customer loyalty and advocacy. For example, we may see a rise in AI-powered systems that can detect and respond to customer emotions, leading to more human-like interactions. This shift will require a workforce upskilling initiative, focusing on the development of soft skills and emotional intelligence amongst customer service representatives.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, implementing the right call center software CRM significantly impacts a business’s success. By carefully considering the factors discussed—from integration challenges and agent performance metrics to security protocols and ROI calculations—businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their customer service operations. Embracing the future trends in this field, such as AI and automation, will further enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction, paving the way for a more streamlined and profitable customer experience.