CRM Software for Call Center Optimization
CRM software for call center operations is revolutionizing customer service. Integrating seamlessly with existing phone systems and IVR, these powerful tools boost agent productivity and efficiency through streamlined workflows and data-driven insights. The right CRM system can significantly improve call handling, leading to happier customers and increased profitability.
This exploration delves into the selection, implementation, and optimization of CRM software specifically designed for call centers, highlighting key features, best practices, and strategies for maximizing return on investment. We will examine various aspects, from choosing the right platform to measuring its impact on key performance indicators.
Call Center Software Features
Effective CRM software significantly enhances call center operations by streamlining processes, improving agent performance, and providing valuable insights into customer interactions. This leads to better customer service, increased efficiency, and ultimately, improved business outcomes. The core functionality centers around managing customer interactions and data, empowering agents, and providing management with actionable intelligence.
Essential Features of Call Center CRM Software
A robust call center CRM system offers a range of features designed to optimize call handling and customer relationship management. These features work in concert to provide a holistic solution for managing interactions, tracking performance, and improving overall efficiency. Key features include contact management, call logging, call recording, automated routing, and integrated communication channels. The system’s ability to manage interactions across multiple channels (phone, email, chat) is crucial for providing seamless customer service. Additionally, features such as agent performance tracking and reporting tools provide valuable data for optimizing processes and improving agent performance.
Integration Capabilities with Existing Call Center Technologies
Seamless integration with existing technologies is paramount for successful CRM implementation in a call center. The CRM system should integrate effortlessly with existing phone systems (e.g., Avaya, Cisco), Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems, and other communication platforms. This integration ensures that all customer interactions are recorded and accessible within the CRM, providing a complete view of the customer journey. For example, integrating the CRM with the phone system allows for automatic logging of calls, pop-up displays of customer information during calls, and efficient call routing based on customer data and agent availability. Integration with IVR systems allows for personalized greetings and efficient call routing based on customer needs.
Improving Agent Productivity and Call Handling Efficiency
CRM software directly impacts agent productivity and call handling efficiency. Features like automated call routing, screen pops displaying customer information, and integrated knowledge bases empower agents to handle calls more efficiently. Automated routing ensures calls are directed to the most appropriate agent based on skills and availability, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. Screen pops displaying customer history and relevant information allow agents to personalize interactions and resolve issues quickly. Access to a centralized knowledge base enables agents to quickly find answers to customer questions, reducing call handling times and improving accuracy. Furthermore, features like call scripting and automated email responses help standardize interactions and improve efficiency.
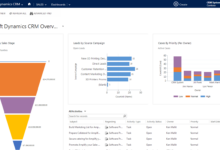
Reporting and Analytics Dashboards for Call Center Management
Data-driven decision-making is crucial for call center success. CRM software provides comprehensive reporting and analytics dashboards that offer real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). These dashboards allow managers to monitor agent performance, identify areas for improvement, and track overall call center efficiency. The data visualized in these dashboards is invaluable for optimizing processes, improving agent training, and enhancing customer service. Customizable dashboards allow managers to focus on the metrics most relevant to their specific goals.
| Metric | Description | Data Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Handle Time (AHT) | Average duration of a customer interaction. | Numeric (seconds/minutes) | 3 minutes 15 seconds |
| Call Abandonment Rate | Percentage of calls abandoned before connecting with an agent. | Percentage | 5% |
| First Call Resolution (FCR) | Percentage of calls resolved on the first attempt. | Percentage | 80% |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | Measure of customer satisfaction with the service received. | Percentage/Score (e.g., 1-5 scale) | 4.5 out of 5 |
CRM Software Selection Criteria
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for a call center’s efficiency and success. A poorly chosen system can lead to decreased productivity, frustrated agents, and ultimately, unhappy customers. The selection process requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure a seamless integration and optimal performance.
Five Critical Factors for CRM Software Selection
Selecting the appropriate CRM hinges on evaluating several critical aspects. These factors directly impact the system’s effectiveness in streamlining operations and improving agent performance. Ignoring these can lead to costly mistakes and integration challenges.
- Integration Capabilities: The CRM must seamlessly integrate with existing call center technologies, such as phone systems (e.g., ACD, IVR), workforce management tools, and other business applications. A lack of proper integration can lead to data silos and inefficient workflows. For example, seamless integration with a phone system allows agents to access customer information directly within their dialer, eliminating the need for manual searches.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting and analytics capabilities are essential for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as call handling time, average handle time (AHT), customer satisfaction (CSAT), and agent productivity. Data-driven insights help identify areas for improvement and optimize call center operations. A CRM lacking this functionality limits the ability to track progress and make informed decisions.
- User-Friendliness and Agent Adoption: The CRM interface should be intuitive and easy for agents to use. A complex or cumbersome system can lead to low adoption rates and decreased productivity. Consider offering training and ongoing support to ensure smooth adoption. A well-designed interface with clear navigation reduces training time and increases agent efficiency.
- Customer Service Features: The CRM should provide tools to enhance customer service, such as omnichannel support (phone, email, chat), self-service options, and knowledge base integration. These features help improve customer experience and reduce resolution times. For example, a built-in knowledge base empowers agents to quickly find answers to common customer queries.
- Security and Compliance: Data security and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) are paramount. The chosen CRM should have robust security features to protect sensitive customer data. Compliance failures can lead to significant fines and reputational damage. Features like data encryption and access controls are critical.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise CRM solutions depends on several factors specific to the call center’s needs and infrastructure.
| Feature | Cloud-Based CRM | On-Premise CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Typically lower upfront costs, subscription-based | Higher upfront investment in hardware and software |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to meet changing needs | Requires significant investment to scale |
| Maintenance | Vendor handles maintenance and updates | In-house IT team responsible for maintenance |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection | Limited to the on-site location |
| Security | Vendor responsible for security, but potential reliance on third-party | Greater control over security, but requires dedicated resources |
Scalability and Customization in Call Center CRM Software
Scalability and customization are critical for long-term success. A scalable CRM can adapt to the call center’s growth, accommodating increasing call volumes and agent numbers without significant disruption. Customization allows the system to be tailored to specific business processes and workflows, enhancing efficiency and improving agent productivity. For instance, a rapidly growing e-commerce company would benefit from a cloud-based CRM that can easily scale to handle a surge in customer inquiries during peak seasons. Conversely, a company with highly specific, niche workflows might benefit from a more customized on-premise solution.
Decision-Making Framework for CRM Software Selection
A structured approach is essential for selecting the optimal CRM. This framework guides the selection process, ensuring alignment with the call center’s specific needs and budget constraints.
- Define Requirements: Clearly outline the call center’s specific needs, including functionalities, integrations, reporting requirements, and scalability expectations.
- Budget Allocation: Determine the budget available for CRM software, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Vendor Evaluation: Research and evaluate potential CRM vendors based on their offerings, reputation, customer support, and pricing models.
- Proof of Concept (POC): Conduct a POC with shortlisted vendors to test the CRM’s functionality and assess its suitability for the call center’s environment.
- Implementation Planning: Develop a detailed implementation plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and training programs for agents.
Implementing CRM in a Call Center
Implementing a new CRM system in a call center requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits. A successful implementation involves strategic steps, from initial assessment to ongoing support, all aimed at improving agent efficiency and customer satisfaction. Failure to properly plan and execute these steps can lead to costly delays, user resistance, and ultimately, a failed CRM project.
Data Migration and Integration Best Practices
Successful data migration is critical for a smooth CRM implementation. Inaccurate or incomplete data can render the system ineffective. Best practices involve a multi-stage approach. First, data cleansing and validation are paramount. This involves identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates within existing customer data. Second, a phased approach to migration minimizes disruption. Start with a pilot group to test the migration process and identify potential issues before migrating the entire dataset. Finally, regular data quality checks and reconciliation post-migration ensure data accuracy and consistency. For example, a call center might begin by migrating data from a specific customer segment before expanding to the entire customer base. This allows for focused problem-solving and refinement of the migration process.
Call Center Agent Training Strategies
Effective training is crucial for maximizing CRM adoption and achieving a positive return on investment. A comprehensive training program should incorporate various methods, such as online modules, hands-on workshops, and ongoing support. Role-playing scenarios can simulate real-world interactions, allowing agents to practice using the CRM effectively. Providing agents with quick reference guides and cheat sheets can address common questions and concerns. Furthermore, establishing a mentorship program pairs experienced agents with newer ones, fostering a collaborative learning environment. For instance, a training program might include interactive tutorials that walk agents through common tasks, followed by a hands-on workshop where they practice those tasks under the supervision of a trainer.
Step-by-Step CRM Integration with Existing Call Center Infrastructure
Integrating a CRM with existing call center infrastructure requires a structured approach. This ensures seamless data flow and avoids disruptions to daily operations.
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough assessment of the existing call center infrastructure, identifying all systems and applications that need to be integrated with the CRM. This includes the phone system (PBX), call recording system, and any other relevant software.
- API Integration: Utilize Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to establish secure and efficient data exchange between the CRM and existing systems. This allows for real-time data synchronization, ensuring information is consistently updated across all platforms.
- Data Mapping: Carefully map data fields between the CRM and existing systems to ensure consistency and accuracy. This involves identifying corresponding fields and ensuring data types are compatible.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the integration process to identify and resolve any issues before full deployment. This involves testing data transfer, functionality, and overall system performance.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the integrated system in a phased manner, starting with a pilot group before expanding to the entire call center. Continuously monitor system performance and data integrity post-deployment to identify and address any potential issues.
Improving Customer Experience with CRM
CRM software revolutionizes call center operations by significantly enhancing customer interactions and boosting overall satisfaction. By centralizing customer data and automating processes, CRM empowers agents to provide more personalized, efficient, and proactive service, ultimately fostering stronger customer relationships and loyalty.
CRM software enhances customer interactions through several key mechanisms. It provides agents with a comprehensive view of each customer’s history, preferences, and past interactions, enabling them to tailor their responses and offer relevant solutions. This personalized approach fosters a sense of value and understanding, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Furthermore, CRM streamlines workflows, reducing wait times and improving response times, which are crucial factors in customer experience. Automated features such as call routing and scripting ensure consistency and efficiency in handling customer inquiries.
Personalized Customer Interactions Using CRM Data
CRM systems offer a wealth of data that can be leveraged to personalize customer interactions. For instance, a customer’s purchase history can be used to offer relevant product recommendations or upselling opportunities. Knowing a customer’s preferred communication method (email, phone, chat) allows agents to contact them through their favored channel. Similarly, access to previous interaction details enables agents to address issues quickly and efficiently, without requiring the customer to repeat information. Imagine a scenario where a customer calls about a recent online order. The CRM system instantly displays the order details, tracking number, and any previous communications related to the order, allowing the agent to address the customer’s concern immediately and avoid frustrating delays. This personalized, informed approach builds trust and strengthens the customer relationship.
Managing Customer Relationships and Resolving Issues Efficiently
CRM plays a vital role in efficiently managing customer relationships and resolving issues. By centralizing all customer data in one place, CRM allows for a 360-degree view of each customer, providing agents with the context needed to handle inquiries effectively. This unified view facilitates faster problem resolution, as agents can access all relevant information without needing to switch between systems or ask repetitive questions. Furthermore, CRM’s case management features allow agents to track the progress of each customer issue, ensuring accountability and timely resolution. The ability to escalate complex issues to supervisors or specialized teams efficiently contributes to a positive customer experience. For example, if a customer has a complex technical issue, CRM can automatically route the call to a technical support team, ensuring that the customer speaks to the right person immediately.
Proactive Customer Service and Anticipating Customer Needs
CRM facilitates proactive customer service by providing insights into customer behavior and potential issues. By analyzing customer data, businesses can identify trends and patterns, allowing them to anticipate customer needs and address potential problems before they escalate. For example, if CRM data reveals a high volume of calls regarding a specific product defect, the company can proactively issue a recall or send out a service advisory, preventing further customer frustration. Furthermore, CRM can be used to trigger automated follow-up messages, such as thank-you notes after a purchase or satisfaction surveys after a service interaction. This proactive approach shows customers that their business is valued and builds loyalty.
Illustration of a Positive Customer Interaction Enabled by CRM
Imagine Sarah, a loyal customer of a telecommunications company, calls to inquire about upgrading her data plan. The agent, using the CRM system, immediately sees Sarah’s account details, including her current plan, past upgrades, and preferred communication method. The agent greets Sarah by name and acknowledges her loyalty, creating an immediate positive connection. The agent then uses the CRM system to show Sarah different upgrade options, highlighting plans that best suit her usage patterns based on her past data consumption. The agent answers all of Sarah’s questions accurately and efficiently, thanks to the readily available information in the CRM system. The entire interaction is smooth, efficient, and personalized, leaving Sarah feeling valued and satisfied. The CRM system also automatically logs the interaction, including the plan upgrade, ensuring seamless follow-up and accurate billing.
Measuring ROI of Call Center CRM
Implementing a CRM system represents a significant investment for any call center. Therefore, accurately measuring its return on investment (ROI) is crucial for justifying the expenditure and demonstrating its value to stakeholders. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), tracking their performance, and analyzing the data to illustrate the positive impact of the CRM system on various aspects of the call center’s operations.
Key Performance Indicators for Call Center CRM ROI
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Effective measurement of CRM ROI requires focusing on specific KPIs that directly reflect the system’s impact on call center efficiency and customer satisfaction. These KPIs should be tracked both before and after CRM implementation to establish a clear baseline for comparison and demonstrate improvement. Examples include:
- Average Handle Time (AHT): This measures the average duration of a customer interaction. A reduction in AHT indicates improved agent efficiency and potentially reduced labor costs.
- First Call Resolution (FCR): This KPI tracks the percentage of calls resolved on the first attempt. Higher FCR rates indicate improved agent knowledge, more efficient processes, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measured through surveys or feedback mechanisms, CSAT reflects the overall customer experience. Improvements in CSAT directly correlate with increased customer loyalty and retention.
- Agent Productivity: This assesses the number of calls handled per agent per hour or day. Increased productivity translates to improved operational efficiency and potentially higher revenue generation.
- Cost per Call: This metric measures the total cost associated with handling each call, including labor, technology, and other expenses. A reduction in cost per call showcases the efficiency gains from CRM implementation.
- Customer Churn Rate: This KPI indicates the percentage of customers who discontinue their service. A lower churn rate suggests improved customer retention due to better service provided through CRM-enhanced processes.
Tracking and Analyzing KPIs
Tracking KPIs requires a robust reporting system integrated with the CRM software. This system should automatically collect data on the aforementioned KPIs, allowing for regular monitoring and analysis. Data visualization tools, such as dashboards and charts, can help to easily identify trends and patterns in the data. Comparative analysis of pre- and post-implementation data is critical to demonstrating the impact of the CRM system. For instance, a 15% reduction in AHT after CRM implementation, coupled with a 10% increase in FCR, provides strong evidence of the system’s positive impact.
Sample ROI Report
The following table illustrates a sample report showcasing the impact of CRM implementation on key call center metrics. Note that these figures are illustrative and will vary depending on the specific call center and CRM system.
| Metric | Before CRM Implementation | After CRM Implementation | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Handle Time (AHT) | 7 minutes | 5.9 minutes | -1.1 minutes (15.7%) |
| First Call Resolution (FCR) | 65% | 75% | +10% |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | 70% | 82% | +12% |
| Agent Productivity (calls/hour) | 6 | 7.2 | +1.2 (20%) |
Strategies for Optimizing CRM Usage
Maximizing CRM ROI requires ongoing optimization and adaptation. This involves regular review of KPI performance, continuous training for call center agents to ensure effective CRM utilization, and proactive identification and resolution of system-related issues. Regular updates to the CRM system and integration with other relevant technologies are also essential for maintaining optimal performance and maximizing the return on investment. For example, integrating the CRM with a knowledge base can drastically improve FCR, while integrating it with a dialer can enhance agent productivity. Furthermore, regular user feedback sessions can help identify areas for improvement in the system’s functionality and user interface, contributing to enhanced user experience and overall effectiveness.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, the successful implementation of CRM software in a call center hinges on careful planning, thorough agent training, and a commitment to continuous optimization. By leveraging the power of data analytics and focusing on key performance indicators, businesses can significantly enhance customer experiences, boost agent productivity, and achieve a substantial return on their investment. The journey towards a more efficient and customer-centric call center begins with the strategic selection and effective deployment of the right CRM solution.