Best CRM Software for Business Success
Best CRM software for business is crucial for growth. Choosing the right system depends heavily on your business size and specific needs. Small businesses might prioritize ease of use and affordability, while larger enterprises require scalability and advanced features like robust reporting and analytics. This guide explores various CRM options, helping you find the perfect fit for your organization, covering everything from initial needs assessment to implementation and ongoing ROI.
We’ll delve into the functionalities you should prioritize—sales automation, marketing campaign management, and efficient customer service tools—and compare leading CRM platforms based on their user interfaces, integration capabilities, and mobile accessibility. Understanding the differences between cloud-based and on-premise solutions is also key, as is considering the vital aspects of data security and privacy.
Defining Business Needs for CRM Software
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for business success. The ideal system seamlessly integrates with your existing workflows, enhances efficiency, and ultimately drives revenue growth. Understanding your specific business needs is the first step in this process. This involves considering your business size, current operational challenges, and future growth aspirations.
Business Size and CRM Requirements
Different business sizes have varying CRM needs. Small businesses often require simpler, more affordable solutions focused on basic contact management and sales tracking. Medium-sized businesses need more advanced features to manage multiple sales teams, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions. Large enterprises require highly scalable and customizable systems to handle complex data, integrate with numerous other applications, and support a global workforce.
Key Functionalities to Prioritize
Prioritizing essential CRM functionalities is key to maximizing ROI. Businesses should focus on features directly addressing their pain points and supporting their strategic objectives. Sales functionalities, such as lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting, are critical for revenue generation. Marketing automation features, including email marketing, campaign management, and social media integration, help nurture leads and build brand awareness. Robust customer service functionalities, like ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and live chat, improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. The selection process should prioritize the functionalities most aligned with the business’s core operations and growth strategy.
CRM Pricing Tiers and Feature Comparison
The following table compares features across three common CRM pricing tiers: Basic, Premium, and Enterprise. Feature availability and pricing vary widely depending on the specific vendor and chosen plan. It is crucial to carefully review the details of each plan before making a purchase decision.
| Feature | Basic | Premium | Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Basic contact storage and organization | Advanced contact segmentation and tagging | Advanced contact management with custom fields and integrations |
| Sales Automation | Basic sales pipeline tracking | Automated sales workflows and reporting | Advanced sales forecasting and analytics, sales territory management |
| Marketing Automation | Limited email marketing capabilities | Automated email campaigns and lead nurturing | Comprehensive marketing automation with A/B testing and advanced analytics |
| Customer Service | Basic ticketing system | Self-service knowledge base and live chat | Advanced customer service features including omnichannel support and case management |
| Reporting and Analytics | Basic sales and marketing reports | Customizable dashboards and advanced reporting | Real-time dashboards and predictive analytics |
| Integrations | Limited integrations | Integration with popular marketing and sales tools | Extensive API access and custom integrations |
| User Support | Email support only | Email and phone support | Dedicated account manager and priority support |
Exploring Top CRM Software Options
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for business success. A well-integrated system streamlines operations, improves customer relationships, and ultimately boosts profitability. This section explores several leading CRM platforms, comparing their features and capabilities to help you make an informed decision.
Leading CRM Software Options Categorized by Focus
Selecting the optimal CRM depends heavily on your business’s specific needs. Prioritizing certain functionalities – sales automation, marketing campaign management, or customer service support – will guide your choice. The following list presents five leading options, each categorized by its primary focus.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: Primarily focused on sales force automation, offering tools for lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. It’s known for its robust features and scalability, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- HubSpot CRM: A strong contender in the marketing and sales arena, HubSpot offers a comprehensive suite of tools including contact management, email marketing, and social media integration. Its free version is attractive for startups and smaller businesses.
- Zoho CRM: A versatile platform offering a blend of sales, marketing, and customer service functionalities. Zoho provides a cost-effective solution with a wide range of features, making it a popular choice for businesses looking for comprehensive functionality without a hefty price tag.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A powerful platform integrating various business applications, including sales, marketing, and customer service modules. Its strength lies in its seamless integration with other Microsoft products, making it a natural choice for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Freshworks CRM: Focused on providing a user-friendly and intuitive platform for managing customer interactions. Its strengths lie in its ease of use and robust customer support capabilities, making it ideal for businesses prioritizing customer service excellence.
Comparison of User Interfaces: Salesforce and HubSpot
Salesforce and HubSpot are two of the most popular CRM platforms. While both offer robust functionalities, their user interfaces differ significantly. Salesforce, known for its powerful features, can present a steeper learning curve with a more complex interface. Its customization options are extensive, allowing for tailoring to specific business needs, but this complexity can initially overwhelm new users. In contrast, HubSpot boasts a more intuitive and user-friendly interface, particularly beneficial for those new to CRM systems. Its clean design and straightforward navigation make it easier to learn and use, although its customization options may be less extensive than Salesforce’s.
Integration Capabilities of Three CRM Systems
Seamless integration with other business tools is vital for maximizing CRM effectiveness. The following details the integration capabilities of three popular systems:
- Salesforce: Salesforce boasts an extensive AppExchange marketplace, offering a vast library of pre-built integrations with email marketing platforms (Mailchimp, Constant Contact), accounting software (Xero, QuickBooks), and other business tools. This allows for a highly customized and interconnected business ecosystem.
- HubSpot: HubSpot’s integration capabilities are deeply embedded within its platform. It offers native integrations with various tools, including Google Workspace, Slack, and several marketing automation platforms. This tight integration ensures smooth data flow between different systems, eliminating manual data entry and improving efficiency.
- Zoho CRM: Zoho CRM offers a robust set of native integrations and also utilizes its own Zoho Marketplace for additional integrations. It integrates well with other Zoho applications, as well as popular tools like Gmail, Google Calendar, and several marketing and accounting platforms. This integrated approach within the Zoho ecosystem can be highly beneficial for businesses already using Zoho products.
Evaluating CRM Software Features
Choosing the right CRM involves a thorough assessment of its features to ensure alignment with your business needs and operational style. Beyond the core functionality, several key aspects significantly impact the overall effectiveness and user experience. Careful consideration of these features will lead to a more informed and ultimately successful CRM implementation.
Mobile Accessibility and its Impact on Productivity
Mobile accessibility is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern CRM systems. The ability to access and update customer information, manage tasks, and respond to inquiries from anywhere, anytime, dramatically boosts productivity. Sales teams can close deals faster by immediately accessing client details on the go. Customer service representatives can resolve issues more efficiently by having real-time access to customer history and support documentation. Furthermore, mobile CRM functionality enhances collaboration, allowing team members to share information and updates regardless of their location. This seamless integration of mobile technology with CRM streamlines workflows and contributes to a more responsive and efficient business operation. For example, a field sales representative can update a customer’s order details immediately after a meeting, ensuring accurate information is readily available for the entire team.
Cloud-Based versus On-Premise CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise CRM solutions presents a significant decision. Cloud-based CRMs, hosted by a third-party provider, offer scalability, accessibility, and reduced upfront costs. However, they introduce dependencies on internet connectivity and may raise concerns regarding data security and control. On-premise solutions, installed and maintained within the company’s infrastructure, provide greater control over data and security but require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel for ongoing maintenance. The optimal choice depends on factors like budget, IT infrastructure, data security requirements, and the level of control desired over the system. For instance, a small business with limited IT resources might find a cloud-based solution more manageable, while a large enterprise with stringent data security policies may prefer an on-premise system.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Data security and privacy are paramount when selecting a CRM system. A robust CRM solution must incorporate multiple layers of security to protect sensitive customer information. The following key considerations should be prioritized:
- Data Encryption: Data both in transit and at rest should be encrypted using strong encryption algorithms to protect against unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure the CRM system complies with relevant data privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, etc.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implement a robust data backup and recovery plan to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or other unforeseen events.
- Vendor Security Practices: Thoroughly vet the CRM vendor’s security practices and certifications to ensure they meet your organization’s security standards.
Implementation and Training
Successfully implementing a new CRM system requires careful planning and execution. A phased approach, coupled with comprehensive employee training, maximizes adoption and minimizes disruption to existing workflows. This section details the crucial steps involved in both implementation and training.
Implementing a new CRM system is a multi-stage process that demands meticulous attention to detail. Ignoring any phase can lead to delays, user frustration, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired return on investment. A successful implementation relies on a well-defined plan and consistent execution.
CRM System Implementation Steps
The implementation process typically involves several key phases. Effective project management, clear communication, and regular progress monitoring are essential for a smooth transition.
- Needs Assessment and System Selection: This initial phase involves a thorough review of business requirements to ensure the chosen CRM system aligns with organizational goals. It includes defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and selecting a system that meets those needs.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing customer data from legacy systems to the new CRM is critical. This process often requires data cleansing and transformation to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Thorough planning and testing are vital to avoid data loss or corruption.
- System Configuration and Customization: This stage involves tailoring the CRM system to meet specific business needs. This may include customizing workflows, dashboards, and reports. Configuration should be aligned with the defined KPIs and user roles.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the CRM with other business systems, such as marketing automation platforms or accounting software, streamlines workflows and improves data consistency. This integration requires careful planning and testing to ensure seamless data flow.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Thorough testing is essential to identify and resolve any bugs or issues before the system goes live. This involves user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the system meets user expectations and requirements.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: The final phase involves launching the new CRM system and providing ongoing support to users. Post-implementation monitoring is crucial to identify and address any unexpected issues or challenges.
Employee Training on CRM Platform
Effective training is paramount to ensure employees can utilize the CRM system efficiently and effectively. A well-structured training program should cover all aspects of the system, from basic navigation to advanced features. The program should also include ongoing support and resources to address user questions and concerns.
- Needs Analysis: Identify specific training needs based on employee roles and responsibilities. Tailor training materials to address these specific needs.
- Training Materials Development: Create comprehensive training materials, including manuals, tutorials, and videos. Ensure materials are easy to understand and visually appealing.
- Training Delivery: Choose a training delivery method that suits the organization’s needs and employee learning styles. Options include instructor-led training, online modules, or blended learning approaches.
- Hands-on Practice: Provide opportunities for employees to practice using the CRM system in a safe environment. This could involve setting up a sandbox environment or using simulated data.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and resources to address user questions and concerns. This could involve creating a knowledge base, providing access to help desk support, or scheduling regular training sessions.
Sample Training Module: Contact Management
This module focuses on effectively managing contacts within the CRM.
- Adding New Contacts: Learn how to input contact information (name, email, phone number, company, etc.) accurately and efficiently. Example: Illustrate the process with screenshots showing the contact form and data fields.
- Searching and Filtering Contacts: Master the techniques for quickly locating specific contacts using various search criteria. Example: Show how to use advanced search filters to find contacts by industry, location, or other relevant parameters.
- Updating Contact Information: Understand the importance of keeping contact information up-to-date. Example: Explain the consequences of outdated information and how to efficiently update contact details.
- Segmenting Contacts: Learn how to group contacts based on shared characteristics for targeted communication. Example: Show how to create segments based on purchase history, demographics, or engagement levels.
- Reporting on Contacts: Understand how to generate reports on contact data for analysis and decision-making. Example: Demonstrate how to create reports showing contact growth, engagement rates, or other key metrics.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Choosing the right CRM system involves careful consideration of its cost and the potential return on that investment. Understanding different pricing models and establishing clear metrics for measuring ROI are crucial for making an informed decision. This section will explore various pricing structures and illustrate how businesses can quantify the benefits of CRM implementation.
Different CRM Pricing Models
CRM software vendors offer a range of pricing models to cater to diverse business needs and budgets. The most common are subscription-based models and one-time purchase models. Subscription models typically involve recurring monthly or annual fees, often tiered based on features, user numbers, or data storage capacity. One-time purchases involve a single upfront payment for the software license, but often require additional fees for support, updates, and upgrades. Some vendors offer hybrid models, combining elements of both approaches.
Subscription-Based Pricing
Subscription-based pricing offers flexibility and scalability. Businesses can easily adjust their plans as their needs change, adding or removing users or features as required. This model is particularly suitable for businesses experiencing rapid growth or those with fluctuating needs. The predictable monthly or annual cost makes budgeting easier. Examples include Salesforce’s various subscription tiers and Zoho CRM’s flexible plans.
One-Time Purchase Pricing
One-time purchase models offer a fixed cost upfront. This can be attractive to businesses with limited budgets or those confident in their long-term needs. However, ongoing maintenance, updates, and support might require additional costs, potentially making the total cost of ownership higher in the long run compared to a subscription model. This model is often less flexible for scaling up or down.
Measuring CRM ROI
Measuring the ROI of a CRM system requires a systematic approach. Businesses can track key performance indicators (KPIs) to quantify the impact of the CRM on various aspects of the business. These KPIs could include improved sales conversion rates, reduced customer acquisition costs, increased customer retention rates, improved sales team productivity, and streamlined customer service processes.
Hypothetical Scenario: Cost Savings with CRM
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario of a small business, “Acme Widgets,” implementing a CRM system. Before implementing the CRM, Acme Widgets experienced high administrative overhead due to inefficient lead management and customer communication. After a year of using the CRM, they see significant improvements.
| Metric | Before CRM | After CRM | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Leads Generated | 500 | 750 | +250 |
| Leads Converted to Sales | 10% | 15% | +5% |
| Average Deal Size | $1000 | $1100 | +$100 |
| Customer Support Costs | $5000/month | $4000/month | -$1000/month |
| CRM Software Cost | $0 | $500/month | +$500/month |
In this scenario, the increased sales and reduced support costs significantly outweigh the cost of the CRM software. The additional revenue generated from the improved conversion rate and average deal size, coupled with the savings in customer support, represents a substantial ROI. The exact figures would depend on the specific business and the CRM system chosen. However, this example demonstrates the potential for significant cost savings and revenue generation through effective CRM implementation.
Illustrative Examples of CRM Software in Action
Seeing CRM software in action helps solidify its value. The following examples demonstrate how businesses of different sizes utilize CRM systems to enhance their operations and achieve specific goals. These scenarios showcase the versatility and impact of CRM across various business contexts.
Small Business Customer Retention with CRM
A small bakery, “Sweet Surrender,” uses a CRM system to track customer orders, preferences, and birthdays. They leverage this information to send personalized birthday emails with a discount code, leading to repeat business and increased customer loyalty. Furthermore, the CRM allows them to segment customers based on purchase history, enabling targeted promotions for specific product lines. For example, customers who frequently buy croissants receive a special offer on a new croissant flavor. This personalized approach fosters a stronger customer relationship, ultimately boosting customer retention rates. Analyzing purchase frequency and customer lifetime value within the CRM provides Sweet Surrender with valuable insights into their most loyal customers, allowing them to focus their marketing efforts effectively.
Large Enterprise Targeted Marketing with CRM Data
A large telecommunications company, “ConnectAll,” uses its CRM system to store vast amounts of customer data, including demographics, usage patterns, and customer service interactions. They segment their customer base into various groups based on these data points, enabling targeted marketing campaigns. For example, customers who frequently use international calling features receive tailored offers for international calling plans. Similarly, customers who have recently experienced technical difficulties receive proactive communications offering support and solutions. ConnectAll uses predictive analytics within their CRM to identify customers likely to churn and proactively addresses their concerns, preventing customer loss. The CRM’s reporting capabilities provide ConnectAll with detailed insights into the success of each campaign, allowing for continuous optimization and improvement of their marketing strategies. This data-driven approach maximizes the effectiveness of their marketing spend and improves customer satisfaction.
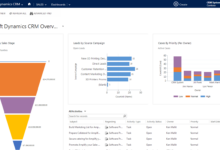
CRM Dashboard KPI Visualization
The CRM dashboard displays key performance indicators (KPIs) in a clear and concise manner. A large central area shows a bar graph representing monthly sales revenue, with individual bars color-coded to show revenue from different sales channels (e.g., online, in-store, phone). Below this, a smaller pie chart displays the distribution of customer acquisition costs across marketing channels. To the right, a dynamic table updates in real-time, showing the number of new leads generated, qualified leads, and deals closed within the current week. A smaller section at the bottom displays a key metric such as customer churn rate, presented as a percentage and a trend line illustrating its movement over the past three months. Color-coding uses green for positive trends and red for negative trends, making it easy to quickly identify areas requiring attention. The dashboard is interactive, allowing users to drill down into specific data points for more detailed analysis.
Closing Notes
Selecting the best CRM software for your business is a strategic decision that impacts efficiency, customer relationships, and ultimately, your bottom line. By carefully evaluating your needs, exploring available options, and planning for implementation and training, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the return on your investment. Remember to prioritize data security and choose a system that scales with your business growth, fostering long-term success and improved customer engagement.